What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Analytics? A Detailed Look

Data analytics has become a cornerstone of modern businesses and organizations, revolutionizing how decisions are made and strategies are formed. From improving operational efficiency to enhancing customer experiences, data analytics offers many advantages. However, it also comes with its own set of challenges and limitations that need to be navigated carefully. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of data analytics, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, ethical considerations, overcoming challenges, and addressing frequently asked questions.
- What Is Data Analytics and How Does It Work?
- What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Analytics?
- Ethical Considerations in Data Analytics
- Overcoming Challenges in Data Analytics
- FAQs about Data Analytics Advantages and Disadvantages
- Conclusion
- Maximize Your Data Impact with BuzzyBrains: Start Making Informed Decisions!
What Is Data Analytics and How Does It Work?
Data analytics is the process of analyzing raw data to uncover meaningful insights, trends, and patterns. It involves various techniques and tools to extract valuable information from large datasets, helping businesses make informed decisions and optimize their operations. The workflow of data analytics typically includes data collection, data cleaning, data transformation, analysis, and interpretation.
Related Blog: Data Analytics: What It Is, How It’s Used, Types, Features, Tools and Techniques
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Analytics?
Data analytics offers a wealth of benefits and opportunities. However, alongside its advantages, it also presents several challenges that organizations must navigate. Let’s examine the advantages and disadvantages of data analytics in more detail.
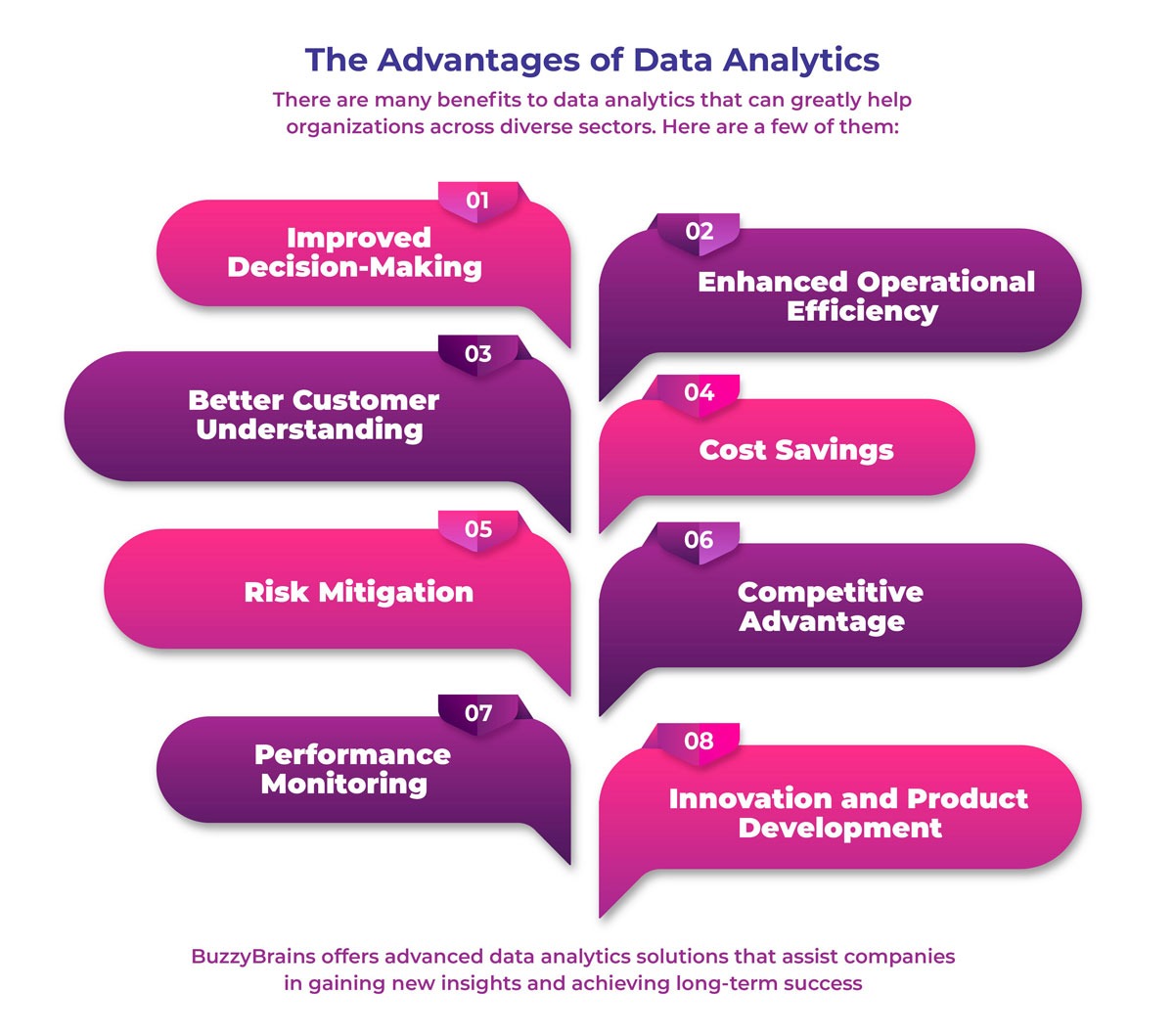
Advantages of Data Analytics
Data analytics offers a plethora of advantages that can significantly benefit organizations. These advantages include enhanced decision-making capabilities through data-driven insights, improved operational efficiency by identifying areas for optimization, a better understanding of customer behaviors and preferences leading to targeted marketing strategies, increased profitability through cost reduction and revenue optimization, and the ability to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market by leveraging data-driven strategies to innovate and adapt. Here’s a detailed look at the advantages of data analytics:
1. Improved Decision-Making:
Data analytics provides valuable insights that enable organizations to make data-driven decisions, reducing guesswork and increasing accuracy. These insights are derived from analyzing large volumes of data, identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that human analysis may overlook.
By leveraging data analytics, decision-makers can access real-time information, predictive models, and visualizations that support informed decision-making across all levels of the organization. This leads to better strategic planning, resource allocation, risk management, and overall business performance.
2. Enhanced Operational Efficiency:
By analyzing operational data, organizations can identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and improve overall efficiency. Data analytics allows businesses to track and monitor key performance metrics, identify inefficiencies, and optimize workflows.
For example, in manufacturing, data analytics can be used to optimize production schedules, reduce downtime, and improve supply chain management. In healthcare, it can help optimize patient flow, resource allocation, and healthcare delivery processes. Overall, data-driven insights enable organizations to operate more efficiently and achieve higher productivity levels.
3. Better Customer Understanding:
Data analytics helps businesses understand customer behavior, preferences, and needs, leading to personalized experiences and improved customer satisfaction. By analyzing customer data such as purchase history, browsing behavior, demographics, and feedback, organizations can segment their customer base, identify trends, and tailor products, services, and marketing strategies accordingly. This personalization enhances customer engagement, loyalty, and retention rates, ultimately driving business growth and profitability.
4. Competitive Advantage:
Organizations that leverage data analytics gain a competitive edge by spotting trends early, identifying market opportunities, and adapting quickly to changes. Data analytics enables businesses to monitor competitor activities, market trends, and consumer sentiment in real-time, allowing them to make agile decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
For example, retail companies can use data analytics to optimize pricing strategies, promotions, and inventory management based on market demand and competitor pricing. Similarly, financial institutions can use data analytics for risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized financial services, gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
5. Risk Mitigation:
Data analytics enables organizations to identify and mitigate risks more effectively by analyzing historical data and predicting future outcomes. By leveraging predictive analytics models, organizations can assess risks related to market fluctuations, customer behavior, operational challenges, and regulatory compliance. This proactive approach to risk management helps organizations anticipate potential issues, implement preventive measures, and make data-driven decisions to mitigate risks and protect their business interests.
6. Cost Savings:
By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving resource allocation, data analytics can lead to significant cost savings for organizations. For example, in supply chain management, data analytics can optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and reduce transportation costs through route optimization and demand forecasting. In healthcare, it can help identify cost-saving opportunities in resource utilization, treatment protocols, and preventive care strategies. By identifying inefficiencies and optimizing resource allocation based on data-driven insights, organizations can achieve cost savings while maintaining or improving operational effectiveness.
7. Innovation and Product Development:
Data analytics fuels innovation by providing insights into market demands, customer feedback, and emerging trends, guiding product development strategies. By analyzing market trends, consumer preferences, and competitor offerings, organizations can identify gaps in the market and develop innovative products or services that meet customer needs.
Data analytics also enables organizations to test and iterate product ideas, gather feedback from early adopters, and optimize product features based on user behavior and preferences. This iterative approach to product development minimizes risks, accelerates time-to-market, and increases the success rate of new product launches.
8. Performance Monitoring:
Organizations can track key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time using data analytics, allowing for proactive decision-making and continuous improvement. By setting measurable KPIs and monitoring performance metrics across departments and functions, organizations can identify trends, anomalies, and areas for improvement.
For example, in sales and marketing, data analytics can track conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and campaign performance, enabling teams to optimize marketing strategies, allocate resources effectively, and achieve sales targets. Similarly, in manufacturing, data analytics can monitor production efficiency, quality metrics, and equipment uptime, facilitating proactive maintenance, process optimization, and overall performance improvement.
Disadvantages of Data Analytics
While data analytics offers numerous advantages, it also comes with several limitations or disadvantages, including the potential for data breaches and security risks, challenges in data quality and accuracy, the need for skilled professionals and resources for implementation, potential biases in data analysis leading to inaccurate conclusions, and the risk of over-reliance on data without considering other factors. Here’s a detailed look at the disadvantages of data analytics:
1. Data Quality Issues:
Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights and flawed decision-making, highlighting the importance of data cleansing and validation. Data may suffer from inconsistencies, errors, duplicates, or missing values, which can skew analysis results and lead to incorrect conclusions.
Data cleansing involves processes such as data deduplication, normalization, validation, and enrichment to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and reliability. Without proper data quality measures, organizations risk making decisions based on flawed or incomplete data, compromising business outcomes.
2. Privacy Concerns:
Collecting and analyzing personal data raises privacy concerns, requiring organizations to comply with data protection regulations and ethical standards. With the increasing volume and sensitivity of data collected, organizations must ensure that data handling practices adhere to privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
This includes obtaining explicit consent for data collection, anonymizing or pseudonymizing data to protect identities, implementing data encryption and access controls, and providing transparency about data usage and rights for data subjects.
3. Complexity and Skill Gap:
Implementing and managing data analytics tools and technologies can be complex, requiring specialized skills and expertise that may not be readily available. Data analytics encompasses a wide range of technologies, including data warehousing, data integration, data mining, machine learning, and data visualization.
Organizations need data scientists, data engineers, analysts, and IT professionals with expertise in these areas to effectively design, implement, and maintain data analytics solutions. The shortage of skilled professionals and the rapid evolution of data analytics technologies can create a significant skill gap and resource challenge for organizations.
4. Cost of Implementation:
The initial investment in data analytics infrastructure, tools, and training can be substantial, especially for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Data analytics requires investments in hardware, software licenses, cloud services, data storage, data processing, and analytics platforms.
Additionally, organizations may need to allocate budget for hiring skilled personnel, conducting training programs, and acquiring external expertise or consultancy services. The cost of implementation and ongoing maintenance can be a barrier for SMBs or organizations with limited resources, impacting their ability to leverage data analytics effectively.
5. Integration Challenges:
Integrating data from disparate sources and systems can be challenging, leading to data silos and inconsistencies. Organizations often have data stored in multiple databases, applications, and platforms, making it difficult to access and analyze data comprehensively.
Data integration involves connecting and harmonizing data from different sources, resolving data format discrepancies, standardizing data models, and ensuring data interoperability. Failure to address integration challenges can result in fragmented data views, duplicate efforts, and inaccurate analysis, hindering data-driven decision-making and insights generation.
6. Bias and Interpretation:
Data analytics results may be influenced by biases in data collection or analysis, leading to biased insights and decisions if not addressed properly. Biases can stem from sample selection, data collection methods, algorithmic biases, or human interpretation of analysis results.
For example, sampling bias can occur if certain demographic groups are overrepresented or underrepresented in the data, skewing analysis outcomes. It’s crucial for organizations to identify, mitigate, and transparently communicate biases in data analytics processes to ensure fair and unbiased decision-making.
7. Security Risks:
Storing and analyzing large volumes of data can pose security risks, such as data breaches and cyber threats, necessitating robust security measures. Data analytics platforms and databases containing sensitive information are attractive targets for cybercriminals seeking to steal data, disrupt operations, or exploit vulnerabilities.
Organizations must implement strong data security measures, including encryption, access controls, data masking, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. Data privacy regulations also mandate data protection practices to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access or disclosure.
8. Lack of Scalability:
Scalability issues may arise as data volumes grow, requiring organizations to invest in scalable infrastructure and solutions. Rapidly increasing data volumes, complex data processing requirements, and evolving business needs can strain existing data analytics systems and architectures.
Organizations must design scalable data pipelines, storage solutions, and analytics platforms that can handle growing data loads, accommodate changing workloads, and deliver performance at scale. Lack of scalability can result in performance bottlenecks, downtime, and limitations on data processing capabilities, limiting the effectiveness of data analytics initiatives.
Addressing these limitations and challenges requires a holistic approach that encompasses data governance, quality assurance, privacy compliance, skills development, technology investments, and risk management. By proactively addressing these issues, organizations can unlock the full potential of data analytics and derive actionable insights that drive business value and competitive advantage.
Ethical Considerations in Data Analytics
When dealing with data analytics, several ethical considerations must be taken into account to ensure responsible and ethical use of data. These considerations include:
- Data Privacy: Respecting individuals’ privacy rights and ensuring data is collected and used in a transparent and lawful manner.
- Data Security: Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
- Fairness and Bias: Mitigating biases in data collection and analysis to ensure fairness and avoid discriminatory outcomes.
- Transparency: Being transparent about data practices, algorithms used, and the purpose of data analytics to build trust with stakeholders.
- Consent and Consent Management: Obtaining informed consent from individuals before collecting and using their data, and providing mechanisms for consent management.
- Compliance: Adhering to data protection regulations, industry standards, and ethical guidelines to ensure compliance and accountability.
Overcoming Challenges in Data Analytics
To overcome the challenges associated with data analytics, organizations can implement several strategies, including:
- Investing in Data Quality: Prioritizing data quality through data cleansing, validation, and governance processes to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Training and Upskilling: Providing training and upskilling programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to leverage data analytics effectively.
- Collaboration and Integration: Encouraging collaboration across departments and integrating data from various sources to break down data silos and improve data consistency.
- Ethics and Governance Frameworks: Establishing ethics and governance frameworks that outline guidelines, policies, and procedures for responsible data use and decision-making.
- Scalable Infrastructure: Investing in scalable infrastructure and cloud-based solutions to handle growing data volumes and ensure flexibility and agility.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, access controls, and threat detection systems, to protect data assets.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Continuously monitoring data analytics processes, identifying areas for improvement, and iteratively refining strategies to enhance outcomes.
FAQs about Data Analytics Advantages and Disadvantages
Q1. What are the advantages of using predictive analytics for forecasting and planning?
Predictive analytics leverages historical data and statistical algorithms to forecast future trends, outcomes, and behaviors. Its advantages include improved accuracy in forecasting, better risk management, and proactive decision-making based on predictive insights.
Q2. How does data analytics help improve decision-making in businesses?
Data analytics provides valuable insights into business performance, customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency, empowering organizations to make informed decisions, identify opportunities, and optimize strategies.
Q3. What impact does data analytics have on improving marketing strategies and ROI?
Data analytics enables marketers to segment audiences, personalize campaigns, measure campaign effectiveness, and optimize marketing strategies based on data-driven insights, leading to improved ROI, customer engagement, and retention.
Q4. What are the limitations of using historical data for predictive analytics?
Using historical data for predictive analytics may have limitations, such as assumptions based on past trends, lack of real-time insights, and the inability to predict unprecedented events or disruptions that deviate from historical patterns.
Q5. How does the complexity of data analytics tools and technologies impact adoption?
The complexity of data analytics tools and technologies can impact adoption by requiring specialized skills, resources, and investments in training and infrastructure. Simplifying user interfaces, providing training and support, and emphasizing the value of data analytics can facilitate adoption.
Conclusion
Data analytics offers significant advantages, including improved decision-making, enhanced efficiency, better customer experiences, and competitive advantages. However, it also presents challenges such as data quality issues, privacy concerns, complexity, and biases. By addressing these challenges, implementing ethical practices, and leveraging data analytics effectively, organizations can maximize the benefits and make data-driven decisions that drive success.
Maximize Your Data Impact with BuzzyBrains: Start Making Informed Decisions!
At BuzzyBrains, we empower businesses with advanced data analytics solutions to unlock insights, drive innovation, and achieve sustainable growth. Our team of experts specializes in data analysis, predictive modelling, machine learning, and data visualization, helping organizations harness the power of data for strategic decision-making. Contact us today to start your data analytics journey and maximize your data impact!